
This varies for different NHS board areas. You may be able to book an appointment for an STI test online using the online booking system. It's less accurate from penile and urine samples. The test is more accurate from vagina samples. In some clinics and at your GP, the swab needs to be sent away to a lab to make the diagnosis. Most sexual health clinics can look at the sample straightaway under the microscope and see the parasite. peeing into a container – this should ideally be done at least 1 or 2 hours after you last peed.using a swab – a small cotton bud is gently wiped over the area that might be infected, such as inside the vagina or penis.There are 2 main ways the sample can be collected: Testing for trichomonas may not be offered in all sexual health clinics. If you think you have trichomonas infection, make an appointment with your GP or local sexual health services. Some women may also experience pain or discomfort during sex. pain or a burning sensation when peeing.Men feel mild discomfort in the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body). genital itching and soreness which can lead to infections of the urethra (the passage that carries pee from the bladder) and infection of the prostate gland Symptoms begin within about 2 to 14 days after infection.a yellow or green discharge from the vagina or penis, which can sometimes have an unpleasant, 'fishy' smell.If you do develop symptoms you may experience:

sharing sex toys that aren't washed or covered with a new condom each time they're usedĪlmost half of all people with trichomonas infection will have no symptoms.having unprotected vaginal, anal or oral sex (sex without a condom).Amount: Some people produce lots of vaginal discharge, while others produce less. If you notice a fishy or foul smell to your discharge and it’s accompanied by changes in texture or color, you may have a vaginal infection. The main way to get trichomonas infection is by: Smell: Vaginal discharge may have an odor, but it shouldn’t be strong and shouldn’t be unpleasant.
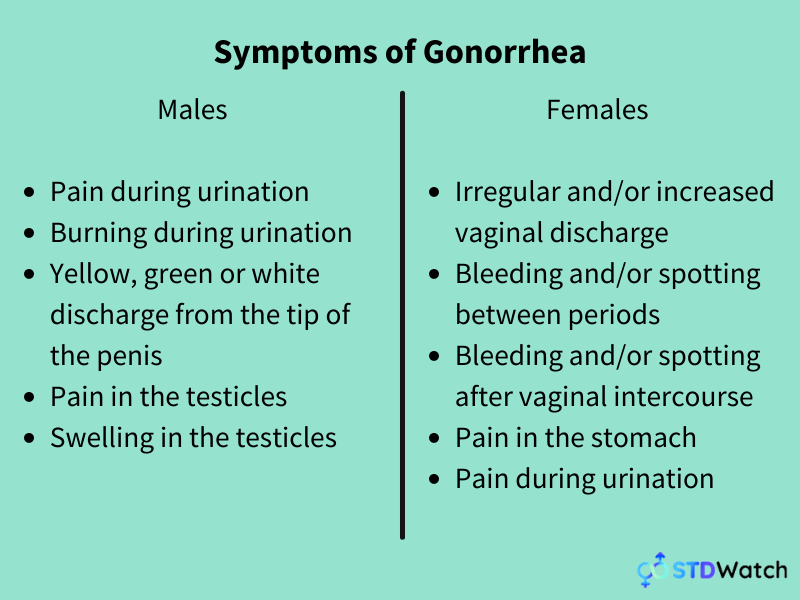
 urethra (the passage carrying urine from the bladder). It infects the genitals and may also lead to infection in the: If you are among those few who develop symptoms (such as painful urination, odd or smelly discharge, or abdominal pain), you will start to notice them between 1. 2021 doi:10.15585/ is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a small parasite. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and nongonococcal urethritis. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection in adults and adolescents. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gonorrhea: CDC fact sheet (detailed version). Alert your sex partners that you're having signs and symptoms so that they can arrange to see their doctors for testing. Have you been exposed to sexually transmitted infections?Ībstain from sex until you see your doctor. Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional?. Questions your doctor is likely to ask you include: If you do experience symptoms, they might include: increased vaginal discharge, often yellow with an unpleasant odor. Are there brochures or other printed material that I can have? What websites do you recommend?ĭon't hesitate to ask other questions. What gonorrhea complications should I be alert for?. How can I prevent gonorrhea in the future?. How long should I wait before resuming sexual activity?. Should my partner be tested for gonorrhea?. Should I be tested for other sexually transmitted infections?. All medications, vitamins or other supplements you take, including dosesįor gonorrhea, questions to ask your doctor include:. Your symptoms, if you have any, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment, and when they began. When you make the appointment, ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as restrict your diet. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment. You'll likely see your family doctor or a general practitioner. Depending on your risk factors, tests for additional sexually transmitted infections could be beneficial as well. Testing for HIV also is recommended for anyone diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition. Gonorrhea increases your risk of these infections, particularly chlamydia, which often accompanies gonorrhea.
urethra (the passage carrying urine from the bladder). It infects the genitals and may also lead to infection in the: If you are among those few who develop symptoms (such as painful urination, odd or smelly discharge, or abdominal pain), you will start to notice them between 1. 2021 doi:10.15585/ is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a small parasite. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and nongonococcal urethritis. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection in adults and adolescents. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gonorrhea: CDC fact sheet (detailed version). Alert your sex partners that you're having signs and symptoms so that they can arrange to see their doctors for testing. Have you been exposed to sexually transmitted infections?Ībstain from sex until you see your doctor. Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional?. Questions your doctor is likely to ask you include: If you do experience symptoms, they might include: increased vaginal discharge, often yellow with an unpleasant odor. Are there brochures or other printed material that I can have? What websites do you recommend?ĭon't hesitate to ask other questions. What gonorrhea complications should I be alert for?. How can I prevent gonorrhea in the future?. How long should I wait before resuming sexual activity?. Should my partner be tested for gonorrhea?. Should I be tested for other sexually transmitted infections?. All medications, vitamins or other supplements you take, including dosesįor gonorrhea, questions to ask your doctor include:. Your symptoms, if you have any, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment, and when they began. When you make the appointment, ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as restrict your diet. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment. You'll likely see your family doctor or a general practitioner. Depending on your risk factors, tests for additional sexually transmitted infections could be beneficial as well. Testing for HIV also is recommended for anyone diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition. Gonorrhea increases your risk of these infections, particularly chlamydia, which often accompanies gonorrhea.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
